Experimental study of the stability and thermophysical properties of PEG400 with CuO and G as a biodegradable nanolubricant
Published 2021-06-28
Keywords
- polyethylene glycol,
- PEG400,
- biodegradable nanolubricants,
- thermal conductivity,
- dynamic viscosity
- stability,
- nanofluids ...More
How to Cite
Copyright (c) 2021 Univiersidad Industrial de Santander

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
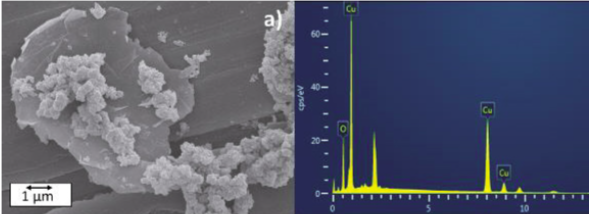
The addition of nanomaterials to conventional lubricants has been presented as an alternative to modify their thermophysical and tribological properties, seeking to increase their performance. This study presents the results of the experimental evaluation of stability, thermal conductivity, and dynamic viscosity of the nanolubricants, PEG400-CuO, PEG400-Graphene and PEG400-CuO / Graphene. The nanolubricants were prepared by the two- step method and two concentrations 0.1 and 0.5 wt.% of each type of nanomaterial were used. The experimental results showed that the dispersions with less agglomeration and sedimentation during the evaluation time were those prepared with 0.1 wt.% of graphene. The thermal conductivity of the PEG400-CuO dispersion did not show significant differences compared to the conductivity of PEG400. However, the conductivity for the PEG400- Graphene and PEG400-CuO / Graphene dispersions (0.5 wt./), increased up to 13.5% and 5.2%, respectively. The dynamic viscosity of the dispersions with a concentration of 0.1 wt.% did not show significant changes with respect to PEG400, while the viscosity of the PEG400-Graphene dispersion (0.5 wt.%) was higher than that of PEG400 for all evaluated temperatures.
Downloads
References
Alemdar, A., Güngör, N., Ece, O. I., & Atici, O. (2005). The rheological properties and characterization of bentonite dispersions in the presence of non- ionic polymer PEG. Journal of Materials Science, 40(1), 171-177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853- 005-5703-4
Azman, N. F., & Samion, S. (2019). Dispersion Stability and Lubrication Mechanism of Nanolubricants: A Review. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing - Green Technology, 6(2), 393-414. https://doi. org/10.1007/s40684-019-00080-x
Babar, H., & Ali, H. M. (2019). Towards hybrid nanofluids: Preparation, thermophysical properties, applications, and challenges. In Journal of Molecular Liquids (Vol. 281, pp. 598-633). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.02.102
Bhaumik, S., Kamaraj, M., & Paleu, V. (2020). Tribological analyses of a new optimized gearbox biodegradable lubricant blended with reduced graphene oxide nanoparticles. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology. https://doi. org/10.1177/1350650120925590
Chen, J., Spear, S. K., Huddleston, J. G., & Rogers, R. D. (2005). Polyethylene glycol and solutions of polyethylene glycol as green reaction media. Green Chemistry, 7(2), 64-82. https://doi.org/10.1039/b413546f
Cortes, V., Sanchez, K., Gonzalez, R., Alcoutlabi, M., & Ortega, J. A. (2020). The performance of SiO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles as lubricant additives in sunflower oil. Lubricants, 8(1). https://doi. org/10.3390/lubricants8010010
Darminesh, S. P., Sidik, N. A. C., Najafi, G., Mamat, R., Ken, T. L., & Asako, Y. (2017). Recent development on biodegradable nanolubricant: A review. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 86(June), 159-165. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2017.05.022
Dhanola, A., & Garg, H. C. (2020a). Influence of different surfactants on the stability and varying concentrations of TiO2 nanoparticles on the rheological properties of canola oil- based nanolubricants. Applied Nanoscience (Switzerland), 0123456789. https://doi. org/10.1007/s13204-020-01467-y
Dhanola, A., & Garg, H. C. (2020b). Materials Today : Proceedings Experimental analysis on stability and rheological behaviour of TiO 2 / canola oil nanolubricants. Materials Today: Proceedings, xxxx. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.245
Geng, Y., Boshra, A. A. A. A. A., Alsagri, A. S., Shahsavar, A., & Talebizadehsardari, P. (2019). Characterization of the nanoparticles , the stability analysis and the evaluation of a new hybrid nano- oil thermal conductivity. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 0123456789. https:// doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08434-y
Gulzar, M., Masjuki, H., Varman, M., Kalam, M., Mufti, R. A., Zulkifli, N., Yunus, R., & Zahid, R. (2015). Improving the AW/EP ability of chemically modified palm oil by adding CuO and MoS2 nanoparticles. Tribology International, 88, 271- 279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2015.03.035
Hemmat Esfe, M., Esfandeh, S., & Rejvani, M. (2018). Modeling of thermal conductivity of MWCNT- SiO2 (30:70%)/EG hybrid nanofluid, sensitivity analyzing and cost performance for industrial applications: An experimental based study. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 131(2), 1437-1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017- 6680-y
Hou, X., Jiang, H., Ali, M. K. A., Liu, H., Su, D., & Tian, Z. (2020). Dispersion behavior assessment of the molybdenum disulfide nanomaterials dispersed into poly alpha olefin. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. molliq.2020.113303
Hu, Y., Wang, Y., Zeng, Z., Zhao, H., Ge, X., Wang, K., Wang, L., & Xue, Q. (2018). PEGlated graphene as nanoadditive for enhancing the tribological properties of water-based lubricant. Carbon, 137, 41-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. carbon.2018.05.009
Huo, M., Wu, H., Xie, H., Zhao, J., Su, G., Jia, F., Li, Z., Lin, F., Li, S., Zhang, H., & Jiang, Z. (2020). Understanding the role of water- based nanolubricants in micro flexible rolling of aluminium. Tribology International, 151(April), 106378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. triboint.2020.106378
Kim, H. J., & Kim, D. E. (2015). Water lubrication of stainless steel using reduced graphene oxide coating. Scientific Reports, 5(C), 1-13. https://doi. org/10.1038/srep17034
Koshy, C. P., Rajendrakumar, P. K., & Thottackkad, M. V. (2015). Evaluation of the tribological and thermo-physical properties of coconut oil added with MoS2 nanoparticles at elevated temperatures. Wear, 330-331, 288-308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. wear.2014.12.044
Kotia, A., Rajkhowa, P., Rao, G. S., & Ghosh, S. K. (2018). Thermophysical and tribological properties of nanolubricants : A review.
León, A., Reuquen, P., Garín, C., Segura, R., Vargas, P., Zapata, P., & Orihuela, P. A. (2017). FTIR and raman characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles coated with polyethylene glycol as carrier for 2-methoxyestradiol. In Applied Sciences (Switzerland) (Vol. 7, Issue 1). https://doi. org/10.3390/app7010049
Liñeira, J. M., Guimarey, M. J. G., Comuñas, M. J. P., López, E. R., Amigo, A., & Fernández, J. (2018). Thermophysical and tribological properties of dispersions based on graphene and a trimethylolpropane trioleate oil. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 268, 854-866. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.07.107
Marcos, M. A., Cabaleiro, D., Guimarey, M. J. G., Comuñas, M. J. P., Fedele, L., Fernández, J., & Lugo, L. (2018). PEG 400-based phase change materials nano-enhanced with functionalized graphene nanoplatelets. Nanomaterials, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8010016
Marcos, M. A., Podolsky, N. E., Cabaleiro, D., Lugo, L., Zakharov, A. O., Postnov, V. N., Charykov, N. A., Ageev, S. V., & Semenov, K. N. (2019). MWCNT in PEG-400 nanofluids for thermal applications: A chemical, physical and thermal approach. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 294, 111616. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111616
Mehrali, M., Sadeghinezhad, E., Latibari, S. T., Kazi, S. N., Mehrali, M., Zubir, M. N. B. M., & Metselaar, H. S. C. (2014). Investigation of thermal conductivity and rheological properties of nanofluids containing graphene nanoplatelets. Nanoscale Research Letters, 9(1), 15. https://doi. org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-15
Mello, V. S., Faria, E. A., Alves, S. M., & Scandian, C. (2020). Enhancing Cuo nanolubricant performance using dispersing agents. Tribology International, 150(March), 106338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. triboint.2020.106338
Nabil, M. F., Azmi, W. H., Hamid, K. A., Zawawi, N. N. M., Priyandoko, G., & Mamat, R. (2017). Thermo- physical properties of hybrid nanofluids and hybrid nanolubricants: A comprehensive review on performance. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 83(March), 30-39. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2017.03.008
Osama, M., Walvekar, R., Khalid, M., Khaliq, A., Yin, W., Chandra, T., & Manikyam, S. (2018). Physical properties optimization of POME-groundnut- naphthenic based graphene nanolubricant using response surface methodology. Journal of Cleaner Production, 193, 277-289. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.070
Pownraj, C., & Valan Arasu, A. (2020a). Effect of dispersing single and hybrid nanoparticles on tribological, thermo-physical, and stability characteristics of lubricants: a review. In Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (Issue 0123456789). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09837-y
Pownraj, C., & Valan Arasu, A. (2020b). Effect of dispersing single and hybrid nanoparticles on tribological, thermo-physical, and stability characteristics of lubricants: a review. In Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (Issue 0123456789). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09837-y
Rostami, S., Ahmadi Nadooshan, A., & Raisi, A. (2020). The effect of hybrid nano-additive consists of graphene oxide and copper oxide on rheological behavior of a mixture of water and ethylene glycol. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 139(3), 2353-2364. https://doi.org/10.1007/ s10973-019-08569-y
Sarkar, J., Ghosh, P., & Adil, A. (2015). A review on hybrid nanofluids: Recent research, development and applications. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 43, 164-177. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.11.023
Soni, S., & Agarwal, M. (2014). Lubricants from renewable energy sources – a review. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 7(4), 359-382. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2014.959565
Suthar, K., Singh, Y., Surana, A. R., Rajubhai, V. H., & Sharma, A. (2020). Experimental evaluation of the friction and wear of jojoba oil with aluminium oxide (Al2O3) nanoparticles as an additive. Materials Today: Proceedings, 25, 699-703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.08.150
Wu, H., Jia, F., Zhao, J., Huang, S., Wang, L., Jiao, S., Huang, H., & Jiang, Z. (2019). Effect of water-based nanolubricant containing nano-TiO 2 on friction and wear behaviour of chrome steel at ambient and elevated temperatures. Wear, 426-427(September 2018), 792-804. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.wear.2018.11.023
Yapici, K., Cakmak, N. K., Ilhan, N., & Uludag, Y. (2014). Rheological characterization of polyethylene glycol based TiO2 nanofluids. Korea Australia Rheology Journal, 26(4), 355-363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-014-0041-1
Yu, W., & Xie, H. (2012). A review on nanofluids: Preparation, stability mechanisms, and applications. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/435873
Zhang, C., Zhang, S., & Song, S. (2014). Preparation and Tribological Properties of Surface-Capped Copper Nanoparticle as a Water-Based Lubricant Additive. 25-33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249- 014-0304-5